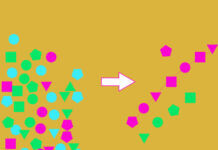
In the realm of IoT development, prototyping is a common starting point. It involves rapid iterations, firmware refinements, and, if applicable, creating a “good enough” Machine Learning (ML) model for deployment. However, as these prototypes evolve into large-scale deployments with hundreds or thousands of devices, challenges arise. Scaling IoT prototypes while preserving the benefits of local, iterative development becomes complicated, especially when it necessitates recalling devices from the field for updates.
This is where MLOps, or Machine Learning Operations, plays a crucial role. MLOps provides a structured approach to streamline the transition of ML-based projects into production, making their management and monitoring more efficient. By adopting MLOps principles, we can continually enhance IoT projects, even after deployment.
How you ask? By using the best of Blues, Edge Impulse, and Zephyr!
By integrating MLOps principles, we can create IoT solutions that can be remotely updated, eliminating the need to recall devices for each improvement.
Join us on this journey to explore:
1. Deploying an “AIoT” project with Edge Impulse and Zephyr: Learn how to combine Edge Impulse’s ML capabilities with Zephyr’s Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) to build robust IoT applications.
2. Remote data accumulation and cloud synchronization with Blues Notecard: Discover how Blues facilitates seamless data synchronization between IoT devices and the cloud, enabling real-time updates and data retrieval.
3. Utilizing new data for cloud-based ML model training: Explore how to use cloud-based ML model training with newly acquired data to continuously enhance IoT applications.
4. Deploying new models while devices are in the field: Learn how to update ML models without physically retrieving devices, ensuring your IoT fleet remains up-to-date.
00:00 Introduction to MLOps
05:55 Getting to Know Cellular IoT with Blues
12:34 Introduction to Zephyr RTOS
23:39 Introduction to ML with Edge Impulse
32:57 Demo Blues, Zephyr, and Edge Impulse ML Model Update